Columnar Transposition Cipher

Introduction
The Columnar Transposition Cipher is a form of transposition cipher just like Rail Fence Cipher. Columnar Transposition involves writing the plaintext out in rows, and then reading the ciphertext off in columns one by one.
Example:
Encryption
Input : Geeks on work
Key = HACK
Output : e w_eoo_Gs kknr_
Decryption
Input : e w_eoo_Gs kknr_
Key = HACK
Output : Geeks on work
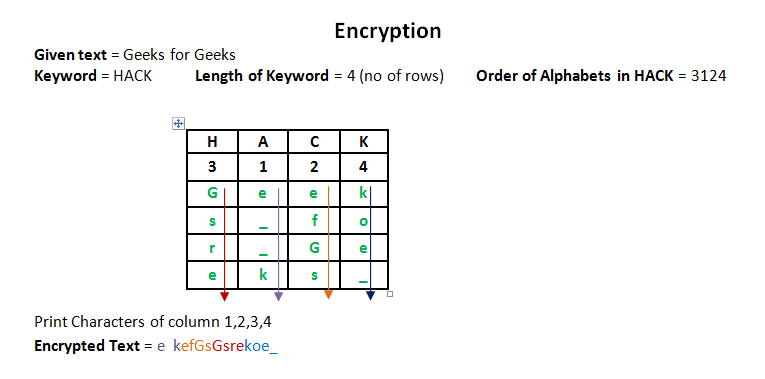
Encryption
In a transposition cipher, the order of the alphabets is re-arranged to obtain the cipher-text.
Decryption
Plaintext:
Key:
Ciphered Text:
Ciphered Text:
Key:
Plain Text: