Caesar Cipher

Introduction
The Caesar Cipher technique is one of the earliest and simplest methods of encryption technique. It's simply a type of substitution cipher, i.e., each letter of a given text is replaced by a letter with a fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example with a shift of 1, A would be replaced by B, B would become C, and so on. The method is apparently named after Julius Caesar, who apparently used it to communicate with his officials.
Thus to cipher a given text we need an integer value, known as a shift which indicates the number of positions each letter of the text has been moved down. The encryption can be represented using modular arithmetic by first transforming the letters into numbers, according to the scheme, A = 0, B = 1,…, Z = 25. Encryption of a letter by a shift n can be described mathematically as.
(Encryption phase with shift n)
(Decryption phase with shift n)
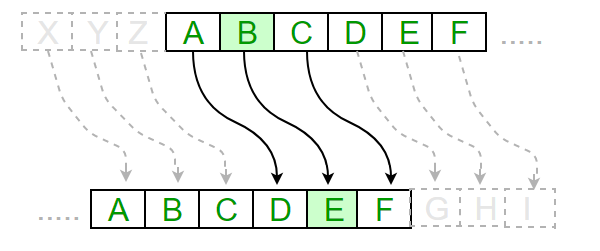
Example:
Text : ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
Shift: 23
Cipher: XYZABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVW
Algorithm for Caesar Cipher
Input:
Procedure:
Plaintext:
Key:
Ciphered Text:
Ciphered Text:
Key:
Plain Text: